News
Study shows links between Australia’s false killer whales and endangered groups from Hawaii
False killer whales off the Northern Australia coast need their conservation status reviewed because of similarities they share with groups from Hawaii listed as Endangered in the USA, a Charles Darwin University (CDU) researcher says.
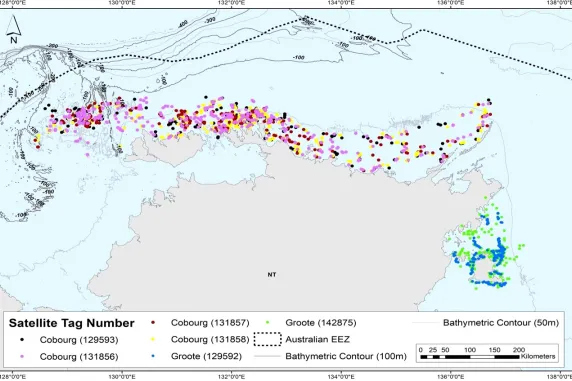
The latest research, published in Frontiers in Marine Science, investigated satellite tag information and DNA samples of the marine mammals from shallow coastal waters from the Cobourg Peninsula in the Northern Territory to the Kimberley region of Western Australia.
In 2012 one of the samples within Port Essington of the Cobourg Marine Park in northern Australia was found to share genetic ancestry with false killer whales found off the coast of Hawaii, and there are other similarities between the groups too.
In Hawaii there are two separate groups of coastal false killer whales - a distinctive species of dolphin - and neither mix with their offshore cousins who live in deep water and this looks like being the case in northern Australia.
Under American legislation however, their false killer whales are labelled as Endangered, whereas in Australia the local populations are listed as Cetaceans, with no Australian Conservation Status.
“We would like to take a precautionary approach and update the conservation status of false killer whales as vulnerable,” said lead researcher, marine biologist Dr Carol Palmer.
“The Australian false killer whales could be genetically unique and also endangered. We need more data to know for sure,” Dr Palmer said.
In Hawaii there are two populations of the coastal false killer whales, one of around 250 individuals and another of about 500.
It is unknown how many are in the Australian populations.
“I think in Australia the populations are naturally small, but we need the funding to get an accurate population estimate,” Dr Palmer said.
The Australian false killer whales seem to travel along the coast, with one tagged individual travelling 7500 kilometres over 105 days, about the same speed as an Olympic long-distance swimmer, she said.
“The tracking and genetic results did show that the false killer whales covered a huge range across Northern Australia.”
First Nations rangers from across the Top End (and the Kimberley), including rangers who were part of the Marine Megafauna workshop and false killer whale research, met at the CDU’s Waterfront campus in mid-February to discuss the findings of this latest study and ongoing marine megafauna work to be carried out in the unique sea country of the NT.
Read the research here.
Related Articles

First “hype cycle” of AI development put tech above humans
Users around the world have rushed to adopt artificial intelligence - especially in safety-critical fields - but a new study has revealed the hype has prioritised technology for technology’s sake instead of human-centred development.
Read more about First “hype cycle” of AI development put tech above humans
Nanoplastics hindering cognitive abilities of fish, international research shows
Nanoplastic exposure can impair the cognitive abilities of fish and could lead to significant impacts on marine species’ ability to survive, according to a new international study.
Read more about Nanoplastics hindering cognitive abilities of fish, international research shows
Eradication would cost billions: NT’s lessons for Pilbara’s cane toad management
Cane toads are predicted to invade Western Australia’s Pilbara region by 2041 if left unchecked, but the Northern Territory’s population of the pests hold key lessons that could save billions in eradication costs.
Read more about Eradication would cost billions: NT’s lessons for Pilbara’s cane toad management